Angioplasty
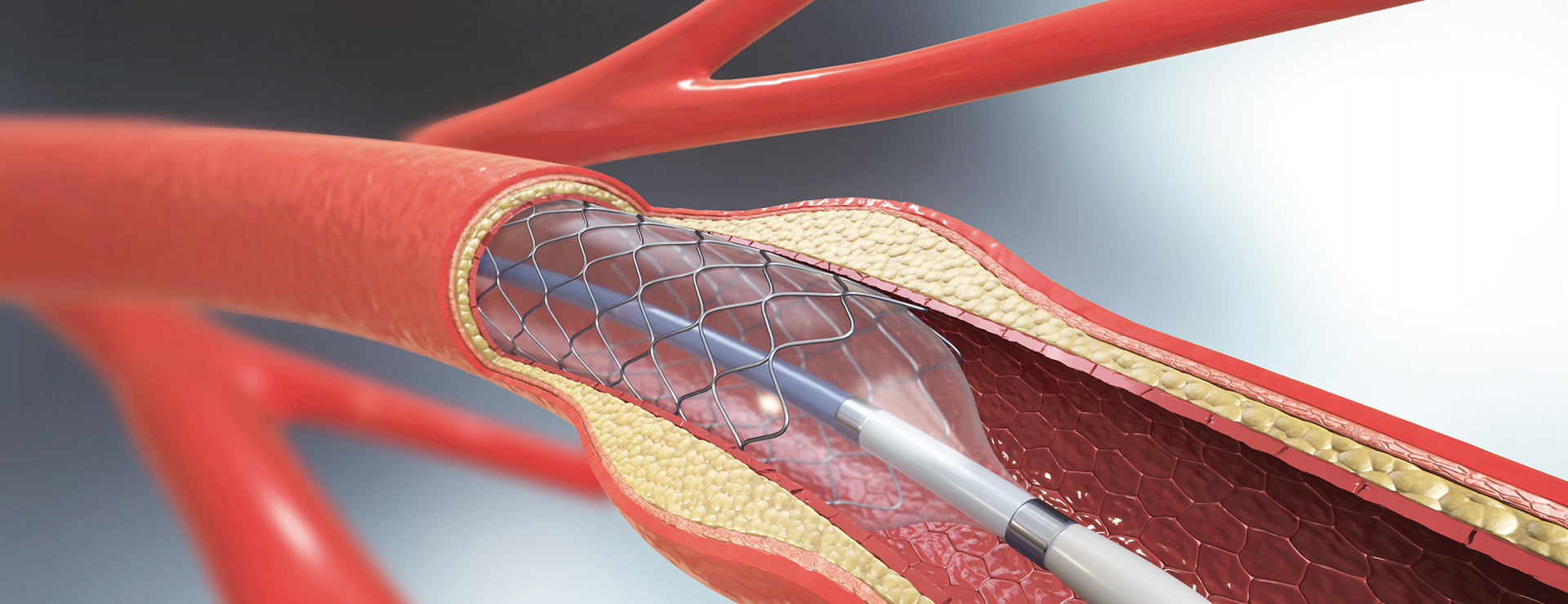
Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat conditions such as atherosclerosis. During angioplasty, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter with a balloon at its tip is inserted into the affected blood vessel. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to compress the plaque or fatty deposits against the artery walls, thereby widening the artery and restoring blood flow. In some cases, a stent (a small mesh tube) may be placed during the procedure to help keep the artery open. Angioplasty is often performed in the coronary arteries of the heart (coronary angioplasty) to relieve symptoms of angina or to treat acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), but it can also be used in other arteries and veins throughout the body.



.png)

