Foot Osteomyelitis
Foot Osteomyelitis encompass a range of structural abnormalities that affect the shape, alignment, and function of the feet. These conditions can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (develop over time) and may include issues such as bunions, hammertoes, flat feet, or clubfoot. Bunions are characterized by a bony bump at the base of the big toe, causing it to lean inward toward the other toes. Hammertoes involve abnormal bending of the toes at the middle joint, resembling a hammer shape. Flat feet, or pes planus, occur when the arches of the feet collapse, causing the entire sole of the foot to touch the ground. Clubfoot is a congenital condition where the foot is twisted out of shape or position, requiring early intervention for correction.
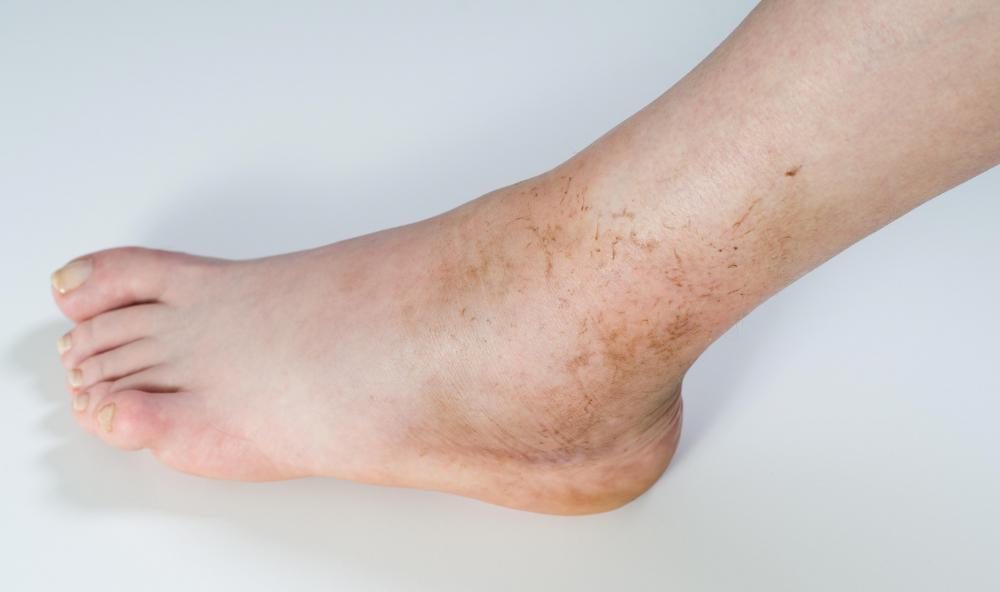
Symptoms of foot osteomyelitis can vary depending on the specific condition but often include pain, discomfort, difficulty walking or wearing shoes, and visible changes in foot shape. Treatment options range from non-surgical approaches such as orthotic devices, supportive footwear, physical therapy, and modifications to lifestyle habits, to surgical interventions aimed at correcting the underlying structural issues. Early diagnosis and appropriate management of foot osteomyelitis are crucial to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall foot function and quality of life.



.png)

