Peripheral vascular disease
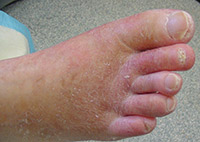
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) refers to conditions that affect the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, primarily the arteries and veins in the arms, legs, and abdomen. This disease often leads to reduced blood flow, causing pain and potentially serious complications.
Common symptoms of PVD include leg pain or cramping during physical activity (claudication), numbness or weakness in the legs, and sores or wounds on the feet that heal slowly. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage symptoms and prevent the progression of the disease. Lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions are employed to improve blood flow and reduce risks.



.png)

